You can turn your skin into screen
Things like these were only the imagination of science fiction authors and movie directors. As a teenager we have at least for one time imagined this thing, that we can turn our skin into a screen. Now, scientists have made this reality. After e-mail, e-book, and e-shopping, now scientists have developed e-skin.
Device that can be sync with the human skin
Scientists from the University of Tokyo, Japan have innovated a new device which can sync with the human skin. The researchers have developed an ultrathin, protective layer that will be helpful in creating “electronic skin” images of oxygen level of blood and other applications. The device will be also useful to the athletes as it will provide e-skin heart rate sensors.
The team of scientists demonstrated the device’s use by creating an air-stable, organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display. The researchers around the world have been trying to combining electronic devices with the human body to increase or restore body function for biomedical applications for a long time.
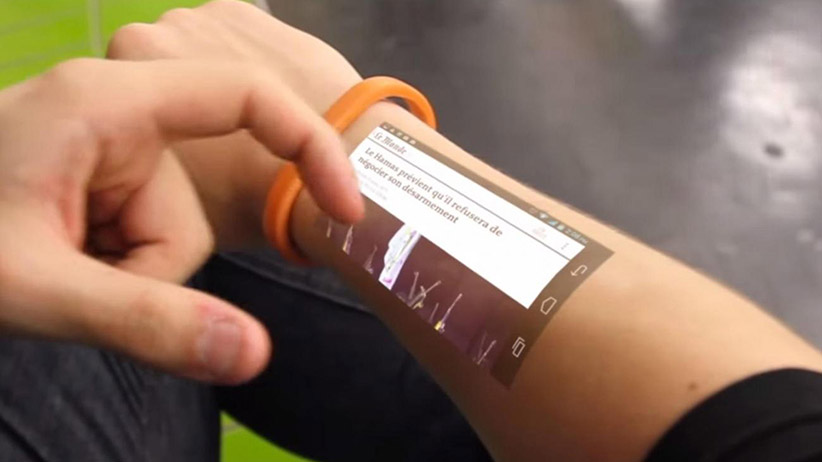

The researchers have taken care of the fact that wearable electronic devices have to be thin and flexible to minimize impact where they attach to the body.
Yet most of the devices developed in the past have demanded millimeter-scale thickness glass or plastic substrates with limited flexibility, while micrometer-scale thin flexible organic devices have proven unstable to work in the air.
Awesome wearable
Professor Takao Someya and Professor Tomoyuki Yokota developed a high-quality protective film which can be wearable. The film was less than two micrometers thick that allow the production of ultrathin, ultra flexible, high performance wearable electronic displays and other devices.
Professor Takao Someya asked, “What would the world be like if we had displays that could adhere to our bodies and even show our emotions or level of stress or unease?”
In a university statement he said, “In addition to not having to carry a device with us at all times, they might enhance the way we interact with those around us or add a whole new dimension to how we communicate.”
The high-quality protective film was successful in preventing passage of oxygen and water vapor in the air, enlarging device lifetimes from the few hours seen in prior research to several days.
how do they did it?
To making the theory of e-skin possible, the group of researchers was able to attach transparent indium tin oxide (ITO) electrodes to an ultrathin substrate without damaging it. In addition, researchers have created polymer light-emitting diodes (PLEDs) and organic photodetectors (OPDs) with the help of new protective layer and ITO electrodes.
The scientists have also combined red and green PLEDs with a photodetector to demonstrate a blood oxygen sensor.
The result was in the favor. The new device was able to attach to the skin. It was also flexible enough to align with the body movements. Now, what makes it particularly suitable for the direct attachment to the body? The answer is the device was fitting perfectly on the human body, and it reduced heat generation and power consumption. So, the device can be used for medical applications such as displays for blood oxygen concentration or pulse rate.
So, now we have a new device to use it for medical purpose. But in future, we should be ready to see a TV screen on our skin because this new discovery has open the doors for lots of possibilities.
